Cosmetics and Personal Care Products also Contain Ethanolamines
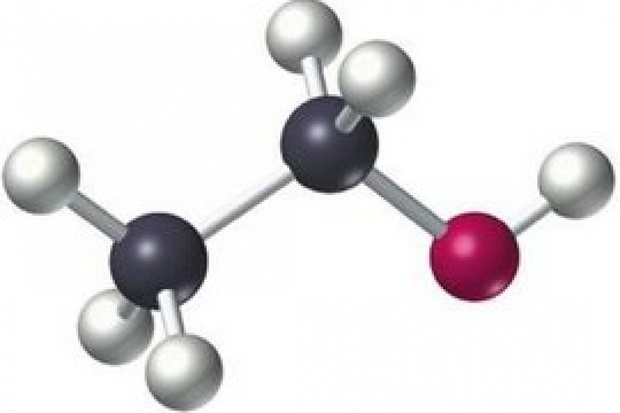
Ethanolamine, commonly known as
2-aminoethanol or monoethanolamine, is an organic chemical molecule that is
both a main amine and a primary alcohol. The substance is known to be
corrosive, combustible, poisonous, colourless, and viscous, and it is utilised
in solutions and dispersions for scrubbing acids, as a feedstock material in
the manufacture of detergents, emulsification agents, and other chemical intermediaries.
Ethanolamines
are chemical compounds with the colourless, viscous HOCH2CH2NH2 molecular
formula. These are utilised as a raw material to produce monoethanolamines
(MEA), diethanolamines (DEA), and triethanolamines (TEA), which are widely used
to make emulsifiers, detergents, polishes, chemical intermediates, corrosion
inhibitors, and medicines.
Due to the amino group in its
molecule, ethanolamine, also known as 2-aminoethanol or monoethanolamine, is an
organic chemical compound that is both a primary amine and a primary alcohol
(due to a hydroxyl group). Monoethanolamine functions as a weak base, just like
other amines. The liquid ethanolamine is poisonous, combustible, corrosive,
colourless, viscous, and has an ammonia-like stench.
To distinguish it from
diethanolamine (DEA) and triethanolamine, ethanolamine is frequently referred
to as monoethanolamine or MEA (TEA). Ethylene oxide and ammonia react to create
monoethanolamine. DEA and/or TEA can be produced with further ethylene oxide
treatment. The second-most prevalent head group for phospholipids, which are
components of biological membranes, is ethanolamine.



Comments
Post a Comment