What is Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring and how it is performed?
 |
| Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Market |
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM) is a diagnostic
procedure that takes readings during regular everyday activities for a period
of 24 hours to assess the existence of hypertension. It aids in the diagnosis
and monitoring of high blood pressure, which is defined as a systolic pressure
of 140 mm Hg or greater and a diastolic pressure of 90 mm Hg or greater.
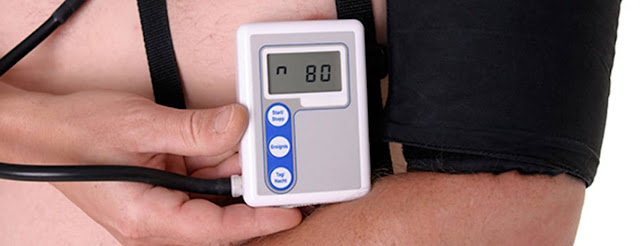
A portable blood pressure machine is employed, which is worn
like a belt with the cuff wrapped around the upper arm. While wearing this
gadget, you can go about your everyday activities normally, including sleeping.
The global
ambulatory blood pressure monitors market size
was valued at US$ 1,135.64 million
in 2018, and is expected to exhibit a CAGR
of 7.9% over the forecast period (2019 – 2027).
At the outpatient clinic, the Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitors
is connected. A digital monitor is utilised in the same way as a cuff inflates
and then slowly deflates in a clinic. During the day, readings are obtained
every 15-30 minutes, and at night, every half-hour to an hour. Throughout the
duration, the cuff is worn, and the machine is kept beneath the pillow or
alongside the patient on the bed as they cheval.
To get a more accurate picture of how blood pressure changes
with different phases of daily activity, the subject getting the measurement
must not disrupt their typical routine. However, because the equipment is
electronic, it cannot withstand water, thus swimming, bathing, or showering
must be avoided for the day. When the machine is withdrawn and returned to the
clinic or hospital, it has the capacity to save all of the readings that are
evaluated. The equipment emits a warning beep when a reading is about to be
taken.



Comments
Post a Comment