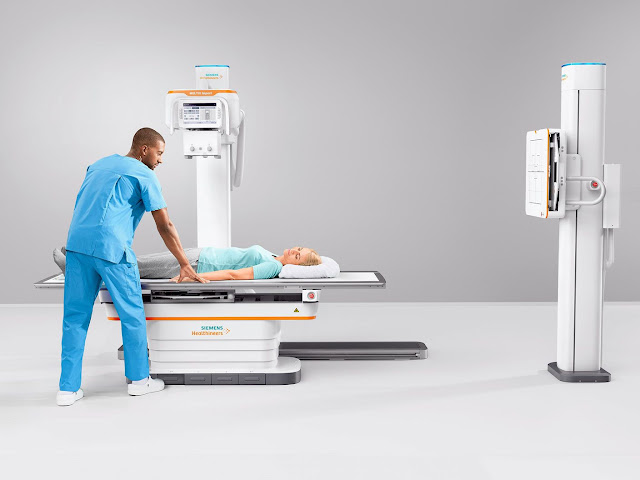
What is Digital Radiography and how does it work?
Digital radiography (DR) may be a form
of x-ray inspection that generates a digital radiographic image on a computer
in real time. During object examination, x-ray sensitive plates capture data,
which is then instantaneously sent to a computer without the necessity of an
intermediate cassette. A detector sensor converts the incident x-ray radiation
into a similar charge, which is then transformed into a digital image.
According to the "Coherent Market Insights" Global Industry Insights, Trends, Outlook, and Opportunity Analysis of Digital Radiography MarketFlat panel detectors, commonly called digital detector arrays (DDAs), deliver high-quality digital images as compared to traditional imaging equipment. They will have the next ratio and a wider dynamic range, leading to increased sensitivity for radiography applications. Indirect conversion and direct conversion are the 2 methods employed by flat panel detectors. Indirect conversion flat panel detectors use a scintillator layer to convert x-ray photons to light photons, which are then converted into an electrical charge by an amorphous silicon photo diode matrix. the number and energy of x-ray photons interacting with the detector pixel, and thus the quantity and density of fabric that has absorbed the x-rays, are proportional to the current charge.
 |
| Digital Radiography Market |
When a flat panel detector is combined with the proper manipulator and image processing software, it are often utilised for x-ray computerized axial tomography (CT) inspection, leading to a 3D image of the test object's external and internal structure.Linear detector arrays are another type of digital x-ray detection media (LDAs). Instead of a matrix, these are made of one row of x-ray detector pixels. to form a 2D radiography image, the LDA or the item under investigation must move relative to every other. LDAs are ideal for inspecting moving things on a conveyor line.



Comments
Post a Comment