Atrial Fibrillation Overview, Symptoms and Preventions
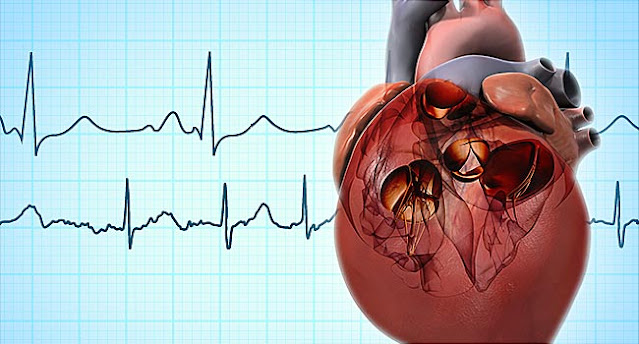
Atrial fibrillation is the most frequent irregular cardiac rhythm that starts in the atria (AF or AFib). Rather than the SA node (sinus node) directing the electrical rhythm, the atria fire multiple different impulses at the same time, resulting in a very fast, chaotic beat. Because the electrical impulses are so fast and disorganised, the atria cannot efficiently contract and/or squeeze blood into the ventricle.
According to the "Coherent Market Insights" Global
Industry Insights, Trends, Outlook, and Opportunity Analysis of Atrial
Fibrillation Market.
Atrial fibrillation (A-fib) is a kind
of arrhythmia (abnormally fast and irregular heartbeat) that can lead to blood
clots in the heart. A-fib increases the risk of stroke, heart failure, and
other heart-related issues. During atrial fibrillation, the upper chambers of
the heart (the atria) beat chaotically and irregularly, out of sync with the lower
chambers (the ventricles). Many people with A-fib don't show any signs or
symptoms. Palpitations (rapid, pounding heartbeat), shortness of breath, and
weakness are all symptoms of A-fib.
Feelings of a racing, fluttering, or
hammering heart (palpitations)
Pain in the chest
Dizziness
Fatigue
Lightheadedness
Exercise ability is hampered.
Breathing problems
Weakness
Atrial fibrillation can be caused by a
variety of factors, including:
On rare occasions (paroxysmal atrial
fibrillation). A-fib symptoms come and go, lasting anything from a few minutes
to many hours. Symptoms might last up to a week, and bouts can occur multiple
times. It's possible that the symptoms will go gone on their own. Some persons
who have A-fib on a regular basis require medical attention.
Persistent. The heart rhythm does not
return to normal on its own in this type of atrial fibrillation. Cardioversion
or pharmacological treatment may be used to restore and maintain a normal heart
rhythm in people who have A-fib symptoms.
Prevention
Healthy lifestyle choices can help
prevent atrial fibrillation and minimise the risk of heart disease. Here are a
few fundamental heart-healthy recommendations:
Consume a healthy diet.
Maintain a healthy weight by
exercising regularly.
Smoking is not permitted.
Caffeine and alcohol should be avoided
or limited.
Manage stress, as high levels of
anxiety and anger can disrupt heart rhythm.



Comments
Post a Comment